NumPy square root
NumPy array class vs python list
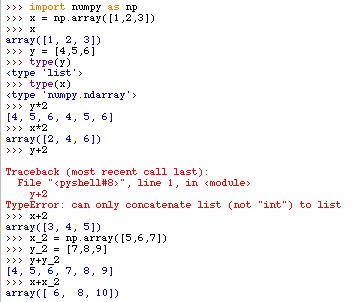
The numpy array is very useful for performing mathematical operations across many numbers. Below you can see that the type list operates very differently than the type numpy.array. Below y is a list and x is a numpy array. Multiplication of lists just repeats the list and addition just concatenates the two lists. However, with the NumPy array component-wise operations are applied.
Unlike lists, all elements of a np.array have to be of the same type. On line 5 below np.array was entered as 1(type int), 2.2(type float), and 3(type int). However, on line 6 it was printed out and you can see all values were converted to type float. Then on line 7 a more complicated component-wise operation was applied to x.

The type of the array can be specified by dtype. Here is a good link for more information on numpy dtype. Below on line 19 the dtype is converted to complex. Then float and int types are used on line 20 and 21 respectively.

Matrices
Matrices are made by adding lists of lists. Below on line 35 is an example of a 3 by 2 matrix. Then the shape of the matrix is revealed on line 37. On line 38 the matrix is transposed. Then matrix multiplication is accomplished on line 40.

Below is an example of dot product.

NumPy has another class called matrix which works similar to matlab. However, I like uses nested lists and NumPy array class better. If you would like to use the NumPy matrix class go to this link for more information.
reshape
flatten
Rank


Linear algebra
How to solve for x in ax = b equation

Eigenvalue

numpy not a number
not a number (NaN) value is a special numerical value. NaN represents an undefined or
unrepresentable value mostly in floating-point calculations. Here is an example for a use
of NaN:
While writing a square root calculator a return of NaN can be used for ensuring the precondition
of x is greater than zero. This is how it could be implemented:
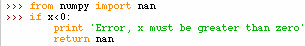
A little more experimenting on numpy nan and python nan concludes that both nans are floating point numbers. Also 'nan' is of type str but float('nan') is type float. However, as expected float('a') can not be converted to a float. From the experiment below you can also see that all floating point numbers return true when you convert to bool type except 0.0.

For more information visit NaN on Wikipedia